Source: Reuters.
A Republican comeback with a new economic strategy
The return of the Republican to the White House heralds an increase in rhetoric against China, contrasting with the more moderate moves of the outgoing Democratic administration. The new president has anticipated greater restrictions on Chinese products and has promised, on his first day in office, to implement tariffs of 25% on Mexico and Canada, in addition to an additional 10% tariff on imports from China.
However, what are the risks of this strategy for the United States? Many economists warn that adopting a trade restriction policy towards Chinese products could have devastating effects on U.S. inflation. This is because these measures will significantly increase the costs of products on American shelves, directly impacting consumers' wallets. In the long term, this increase in costs could reduce the purchasing power of American families, especially those in the most vulnerable sectors. It could also trigger a chain reaction, with companies passing on their additional costs to consumers or reducing their workforce to remain competitive.
In this struggle to bring industry back to the West, particularly to the United States, and to revitalize employment in the country to "Make America Great Again," the president's efforts seem to face a significant challenge. This is due to the consolidated Chinese dominance over the past two decades and its growing global expansion, not only as an industrial power but also as an alternative market for countries excluded from the Western economic system, such as Russia and Iran. This context places the United States in a position where competing directly with China requires not only protectionist policies but also a structural reinvention in its industrial and economic sectors.
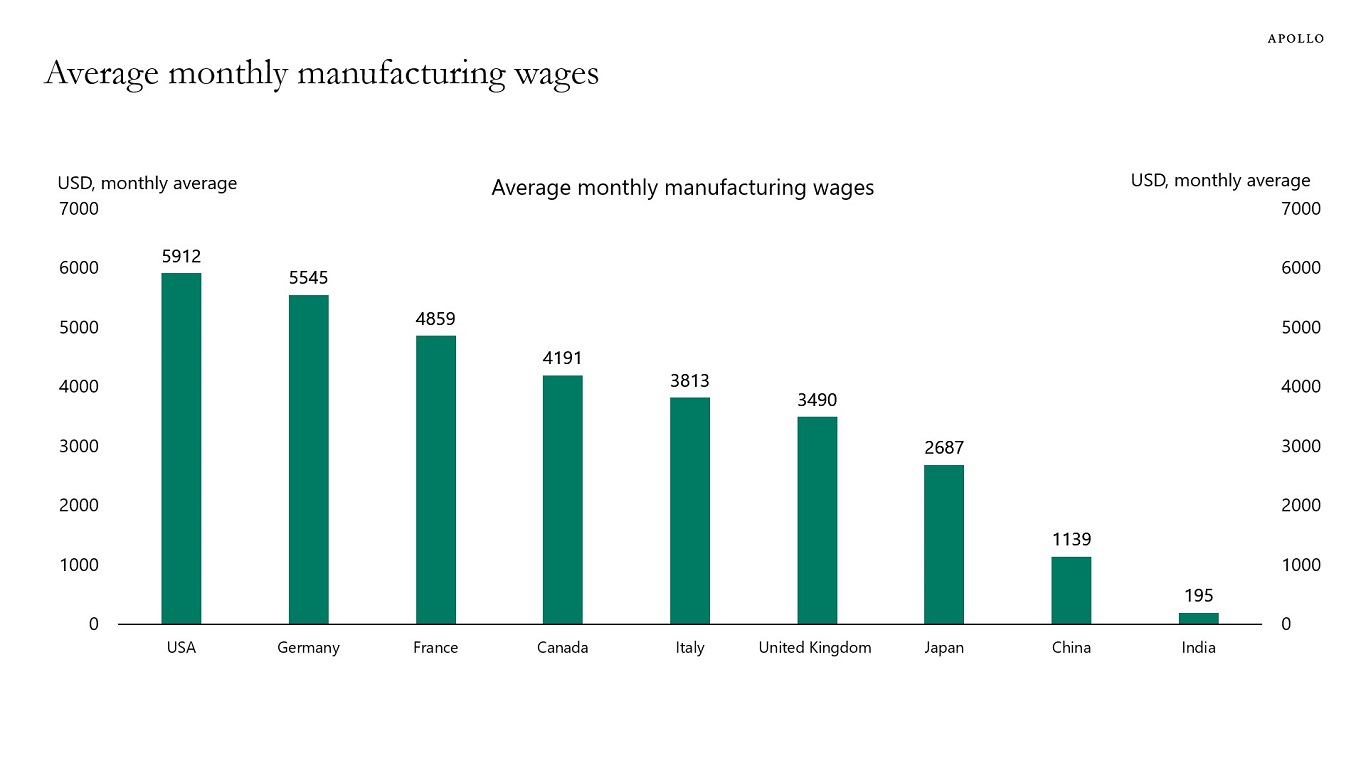
Source: APOLLO
Another of the inherent problems with this strategy is the disparity in industrial wages between the United States and China. While in the United States the average salary in the industry is around $6,000 per month, in China it is only $1,140. This difference highlights the strong competitive capacity of the Asian giant compared to the United States. Additionally, China has complemented its low labor costs with massive investments in infrastructure, technology, and technical education, further strengthening its position as a global manufacturing leader.
To counter this advantage, the United States could consider strategies that go beyond lowering production costs. These include tax incentives for companies that invest in advanced technologies and renewable energies, as well as training programs for the workforce in strategic sectors such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology. These measures, while costly in the short term, could position the United States as a more innovative and sustainable competitor against China.
On the other hand, a drastic regulatory reduction policy, such as that proposed by the "Department of Government Efficiency" (DOGE) led by Elon Musk, can create both opportunities and risks. Regulatory easing could stimulate business activity, but it could also compromise environmental protection and labor rights, generating social and political tensions. Moreover, the exclusive focus on economic efficiency could overlook other key factors, such as social cohesion and political stability, which are essential for long-term success.
Ultimately, the strategy to make the United States competitive against China will require a balance between protectionist measures, incentives for innovation, and social policies that minimize the negative effects on the population. The success of this initiative will depend not only on government decisions but also on the ability of public and private sectors to adapt to the challenges of the constantly evolving global economic landscape.
To embark on a second trade war, the United States would need to implement a significant reduction in its production costs. It is in this context that other key players come into play, whose role could determine the success or failure of this strategy.
'DOGE': A bet on government efficiency
In this particular strategy, and according to the epic rhetoric of Trumpism, the mogul and owner of the social network X (formerly Twitter), Elon Musk, would play a crucial role. In addition to significantly multiplying his already enormous fortune after Trump's eventual victory, Musk would be in charge of the newly created "Department of Government Efficiency" (DOGE, for its initials in English).
This department would have the mission of applying a "chainsaw" to public spending and economic regulations, aimed at drastically reducing production costs in the United States. According to projections from its supporters, this policy would foster the reindustrialization of the country, attracting investments and promoting job creation in key sectors, such as technology, manufacturing, and energy. However, critics warn that this strategy could have serious side effects, such as weakening the purchasing power of wages and increasing prices in the medium term.
Furthermore, the reduction of environmental regulations, often proposed as part of these reforms, raises additional concerns. While it could accelerate industrial projects, it could also negatively impact efforts to combat climate change and preserve natural resources. These tensions between economic competitiveness and environmental sustainability could become a point of friction both domestically and internationally.
On the other hand, the focus on decreasing production costs in the United States must confront the realities of the global market, where China not only dominates due to its low labor costs but also because of its efficient infrastructure and ability to adapt its economy rapidly. In this sense, some analysts suggest that the United States would need to combine these reforms with strong incentives for innovation and education, striving to maintain its technological advantage in strategic areas such as artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and renewable energies.
Ultimately, it remains uncertain whether a massive "chainsaw" approach to public spending and regulations will be sufficient to make the United States as competitive as China, or if this strategy risks weakening the structural foundations of its economy in the long run. The direction this policy takes will depend not only on government decisions but also on the response of economic actors, social movements, and international markets.
If you are interested in learning more about how artificial intelligence tools can transform your daily tasks, we invite you to participate in the course "AI Tools." In this course, you will explore applications that facilitate content creation, text correction, and presentation design. Discover how to optimize your creative and productive processes with the latest generative technologies. Don't miss out!

Comments